


Where:
ρ= the density of the air
A= the swept area of the blades
V= the velocity of the wind
Notes:
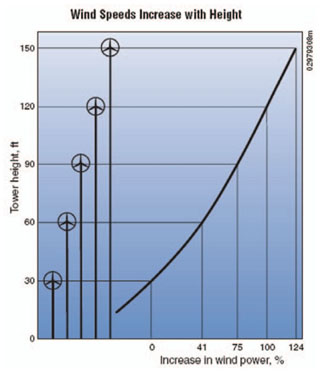
V: As the velocity increases, power will increase exponentially. This section of the equation highlights the importance of height of the turbine pole.
A: as the blade size increases, the radius of the windswept are increases, resulting in an exponential increase in area. As area increases, so does the power.
ρ: (rho) The density of the air changes during the year. When temperatures are colder, air compresses, and becomes denser. Therefore turbines actually produce more power in the winter, and can provide a nice complement for solar energy.
The power equation calculates wind power for a specific wind speed. In order to determine if wind is viable, a site must have a sufficient wind power density.
Image Source: American Wind Energy Association
Wind Power